以前から気になっていた Direct Routing (a.k.a. DSR, Direct Server Return) 方式のロードバランサーの挙動を確認しました。以下の書籍で Network Namespace で実験する方法を習得したので、仮想マシンを複数用意することなく手軽に実験できました。
Direct Routing の仕組み
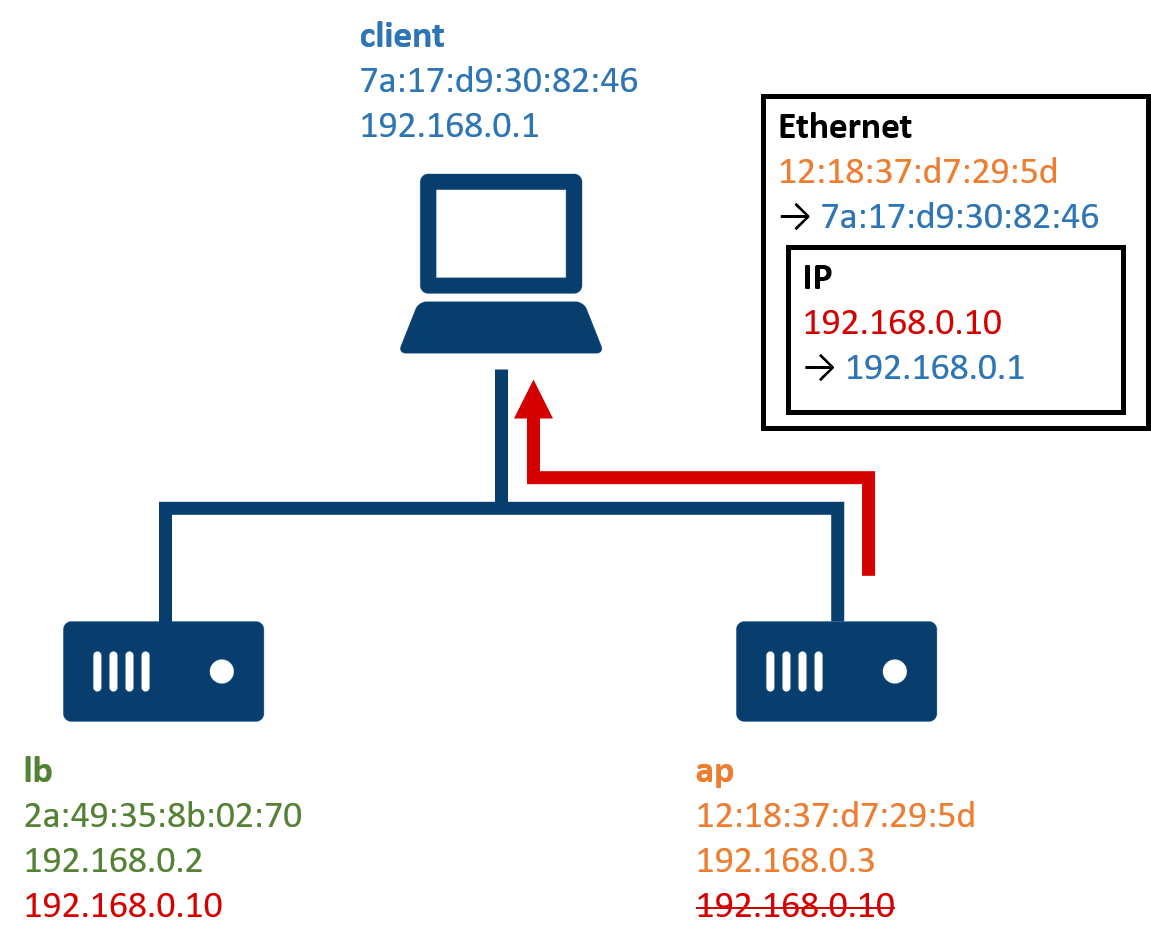
以下のようなネットワークがあるとします。lb = ロードバランサー、ap = アプリケーションサーバーです。3台のホストはすべて同じネットワークセグメントに所属しています。アプリケーションサーバーが1台しかないのにロードバランサーを使う必要があるのかという疑問が浮かぶかもしれませんが、これは Direct Routing の仕組みを知る上では台数はあまり関係がないためです。

lb と ap には、そのサーバー固有のリアル IP アドレス(ここでは 192.168.0.2 と 192.168.0.3)のほかに、ロードバランシングされる IP アドレスとしてクライアントから利用されることを意図したバーチャル IP アドレス(VIP、ここでは 192.168.0.10)を付与します。何も対策しない状態では同じネットワークセグメントに同じ IP アドレスを持つホストが複数存在する状態となり問題が起きるので、ap 側の VIP には後述する特殊な細工を行っています。

クライアントから VIP を指定してサービスにアクセスする例を見てみます。ap 側の VIP には特殊な細工を行っているため、VIP へのアクセスは lb に向けられます。

ここで lb によってトラフィックの振り分けが行われます。ap にトラフィックが向けられるときは Ethernet フレームの宛先 MAC アドレスが ap のものに書き換えられ、IP パケットの中身はそのまま転送されます。

クライアントへのレスポンスの戻り方が Direct Routing の最も特徴的な点です。lb から ap へは IP パケットの中身がそのまま転送されたので、ap が受け取ったリクエストの送信元 IP アドレスはクライアントの IP アドレスとなっています。よって、リクエストを受け取ったアプリケーションは「送信元の IP アドレスにレスポンスを返す」という通常の動作をするだけで、lb を迂回して直接クライアントにレスポンスを返すことができます。
Direct Routing の利点と欠点
レスポンスを返すときに lb を迂回して直接クライアントに返すことができるという点が最も大きな利点です。Web のトラフィックはサーバーの視点ではリクエストよりもレスポンスのほうが大きくなることが普通なので、lb のボトルネックが緩和されることが期待できます。
副次的な効果として ap から見た送信元 IP アドレスがクライアントの IP アドレスになる点もあります。NAT モードなどと呼ばれている方法では ap から見た送信元 IP アドレスが lb のものになってしまうため、クライアントの IP アドレスを利用する諸々の処理(たとえばアクセスログの保存や IP アドレスを使ったアクセスブロック)に制限があります。
欠点としてはロードバランサーとアプリケーションサーバーが同じネットワークセグメントに所属していない場合には利用できません。
環境の作成
動作は Ubuntu 20.04 LTS で確認しました。
最初に client, lb, ap の namespace を作成してブリッジに接続し、IP アドレスを付与します。
# namespace の作成 $ sudo ip netns add client $ sudo ip netns add lb $ sudo ip netns add ap $ ip netns ap lb client # ブリッジと接続するインターフェースを作成 $ sudo ip link add client-veth0 type veth peer name client-br0 $ sudo ip link add lb-veth0 type veth peer name lb-br0 $ sudo ip link add ap-veth0 type veth peer name ap-br0 # 作成したインターフェースを対応する namespace に接続して UP に設定する。 $ sudo ip link set client-veth0 netns client $ sudo ip link set lb-veth0 netns lb $ sudo ip link set ap-veth0 netns ap $ sudo ip netns exec client ip link set client-veth0 up $ sudo ip netns exec lb ip link set lb-veth0 up $ sudo ip netns exec ap ip link set ap-veth0 up # IP アドレスを設定する $ sudo ip netns exec client ip addr add 192.168.0.1/24 dev client-veth0 $ sudo ip netns exec lb ip addr add 192.168.0.2/24 dev lb-veth0 $ sudo ip netns exec ap ip addr add 192.168.0.3/24 dev ap-veth0 # ブリッジを作成して UP に設定する $ sudo ip link add br0 type bridge $ sudo ip link set br0 up # インターフェースの対向側をブリッジに接続して UP に設定する。 $ sudo ip link set client-br0 master br0 $ sudo ip link set lb-br0 master br0 $ sudo ip link set ap-br0 master br0 $ sudo ip link set client-br0 up $ sudo ip link set lb-br0 up $ sudo ip link set ap-br0 up $
アプリケーションサーバー(リアルサーバー)の設定
動作確認の都合上、ロードバランサーの設定をするよりも先にアプリケーションサーバーの設定をしたほうがよいことが分かったのでこちらを先に実施します。
冒頭で ap に付与する VIP には特殊な細工が必要だと説明しました。これはクライアントから VIP に接続しようとしたとき、lb と ap の両方が ARP リクエストに応答してしまい、本来 lb に向けられなければならないトラフィックがリアルサーバーに向けられてしまうためです。これを回避する方法としては arptables を使って ARP リクエストをフィルタリングする方法 などもありますが、よく見かける方法はループバックインターフェースに VIP を付与した上で、ARP に応答する IP アドレスをインターフェースに紐づけられたものに限定する設定を行うという方法です。
まず ap の lo に VIP を付与します。
$ sudo ip netns exec ap ip addr add 192.168.0.10 dev lo
$ sudo ip netns exec ap ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 192.168.0.10/32 scope global lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
17: ap-veth0@if16: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 12:18:37:d7:29:5d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 192.168.0.3/24 scope global ap-veth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::48eb:fff:fe39:9f0c/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
$
ap で tcpdump を実行した状態で client から VIP に ping を打ってみます。
$ sudo ip netns exec client ip neigh flush all $ sudo ip netns exec client ping -c1 192.168.0.10 PING 192.168.0.10 (192.168.0.10) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.0.10: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.054 ms --- 192.168.0.10 ping statistics --- 1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.054/0.054/0.054/0.000 ms $ sudo ip netns exec client ip neigh 192.168.0.10 dev client-veth0 lladdr 12:18:37:d7:29:5d REACHABLE $
$ sudo ip netns exec ap tcpdump -tnel tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on ap-veth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff, ethertype ARP (0x0806), length 42: Request who-has 192.168.0.10 tell 192.168.0.1, length 28 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, ethertype ARP (0x0806), length 42: Reply 192.168.0.10 is-at 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, length 28 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 192.168.0.1 > 192.168.0.10: ICMP echo request, id 4539, seq 1, length 64 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 192.168.0.10 > 192.168.0.1: ICMP echo reply, id 4539, seq 1, length 64
ap が VIP に対する ARP リクエストに応答してしまいました。client の ARP テーブルには 192.168.0.10 に対応する MAC アドレスとして ap-veth0 の 12:18:37:d7:29:5d がばっちり記録されてしまっています。
これはまずいので lo に付与した VIP の ARP リクエストを ap-veth0 から受け取っても応答しない設定を入れます。arp_ignore=1 を設定すると、IP アドレスを付与したインターフェース以外からの ARP リクエストには応答しなくなります。
$ sudo ip netns exec ap sysctl net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore=1 net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1 $
ap で tcpdump を実行した状態で client から VIP に ping を打ってみます。
$ sudo ip netns exec client ip neigh flush all $ sudo ip netns exec client ping -c1 192.168.0.10 PING 192.168.0.10 (192.168.0.10) 56(84) bytes of data. ^C --- 192.168.0.10 ping statistics --- 1 packets transmitted, 0 received, 100% packet loss, time 0ms $ sudo ip netns exec client ip neigh 192.168.0.10 dev client-veth0 FAILED $
$ sudo ip netns exec ap tcpdump -tnel tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on ap-veth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff, ethertype ARP (0x0806), length 42: Request who-has 192.168.0.10 tell 192.168.0.1, length 28 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff, ethertype ARP (0x0806), length 42: Request who-has 192.168.0.10 tell 192.168.0.1, length 28 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff, ethertype ARP (0x0806), length 42: Request who-has 192.168.0.10 tell 192.168.0.1, length 28
ap が VIP の ARP リクエストに応答しないことが確認できました。ただし、これだけではまだ問題があります。ap から client にレスポンスを返すために、ap が client の MAC アドレスを得るための ARP リクエストを送信すると、そのリクエストの送信元 IP には VIP が付与されてしまいます。
client で tcpdump を実行した状態で ap から client に ping を打ってみます。ただし ICMP の送信元 IP アドレスには VIP を使います。
$ sudo ip netns exec ap ip neigh flush all $ sudo ip netns exec ap ping -c1 -I192.168.0.10 192.168.0.1 PING 192.168.0.1 (192.168.0.1) from 192.168.0.10 : 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.053 ms --- 192.168.0.1 ping statistics --- 1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.053/0.053/0.053/0.000 ms $
$ sudo ip netns exec client tcpdump -tnel tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on client-veth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff, ethertype ARP (0x0806), length 42: Request who-has 192.168.0.1 tell 192.168.0.10, length 28 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype ARP (0x0806), length 42: Reply 192.168.0.1 is-at 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, length 28 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 192.168.0.10 > 192.168.0.1: ICMP echo request, id 4681, seq 1, length 64 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 192.168.0.1 > 192.168.0.10: ICMP echo reply, id 4681, seq 1, length 64
"Request who-has 192.168.0.1" という ARP リクエストに VIP の 192.168.0.10 に対応する MAC アドレスが 12:18:37:d7:29:5d であるという情報が乗ってしまいました。さらに悪いことに、ap から ping を打った直後に client の ARP テーブルを調べると VIP と MAC アドレスの関係が記録されてしまっています。
$ cat run.sh #!/bin/bash set -x sudo ip netns exec client ip neigh flush all sudo ip netns exec ap ip neigh flush all sudo ip netns exec ap ping -c1 -I192.168.0.10 192.168.0.1 sudo ip netns exec client ip neigh sudo ip netns exec client ping -c1 192.168.0.10 $ bash run.sh + sudo ip netns exec client ip neigh flush all + sudo ip netns exec ap ip neigh flush all + sudo ip netns exec ap ping -c1 -I192.168.0.10 192.168.0.1 PING 192.168.0.1 (192.168.0.1) from 192.168.0.10 : 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.044 ms --- 192.168.0.1 ping statistics --- 1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.044/0.044/0.044/0.000 ms + sudo ip netns exec client ip neigh 192.168.0.10 dev client-veth0 lladdr 12:18:37:d7:29:5d DELAY + sudo ip netns exec client ping -c1 192.168.0.10 PING 192.168.0.10 (192.168.0.10) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.0.10: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.026 ms --- 192.168.0.10 ping statistics --- 1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.026/0.026/0.026/0.000 ms $
これを回避するために、arp_announce=2 という設定を入れて ARP リクエストを送信するときにはそのインターフェースの IP アドレスを利用するようにします。
$ sudo ip netns exec ap sysctl net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce=2 net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2 $ sudo ip netns exec ap ip neigh flush all $ sudo ip netns exec ap ping -c1 -I192.168.0.10 192.168.0.1 PING 192.168.0.1 (192.168.0.1) from 192.168.0.10 : 56(84) bytes of data. ^C --- 192.168.0.1 ping statistics --- 1 packets transmitted, 0 received, 100% packet loss, time 0ms $
$ sudo ip netns exec client tcpdump -tnel tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on client-veth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff, ethertype ARP (0x0806), length 42: Request who-has 192.168.0.1 tell 192.168.0.3, length 28 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype ARP (0x0806), length 42: Reply 192.168.0.1 is-at 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, length 28 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 192.168.0.10 > 192.168.0.1: ICMP echo request, id 4761, seq 1, length 64 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff, ethertype ARP (0x0806), length 42: Request who-has 192.168.0.10 tell 192.168.0.1, length 28
ap からの ARP リクエストに乗せられる IP アドレスが 192.168.0.3(ap-veth0 に付与された IP アドレス)になりました。
ところで、lo に付与された VIP への通信を ap-veth0 で受け取れるのかという疑問が湧いてきますが、不思議なことに Linux では、あるインターフェースに付与された IP アドレスとの通信を別のインターフェースで行うことができるようになっているようです。試しに VIP の ARP テーブルを手動で作成すると client から ap に通信することができます。
$ sudo ip netns exec client ip neigh flush all $ sudo ip netns exec client ip neigh add 192.168.0.10 lladdr 12:18:37:d7:29:5d dev client-veth0 $ sudo ip netns exec client ip neigh 192.168.0.10 dev client-veth0 lladdr 12:18:37:d7:29:5d PERMANENT $ sudo ip netns exec ap ip neigh flush all $ sudo ip netns exec client ping -c1 192.168.0.10 PING 192.168.0.10 (192.168.0.10) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.0.10: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.064 ms --- 192.168.0.10 ping statistics --- 1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.064/0.064/0.064/0.000 ms $
$ sudo ip netns exec ap tcpdump -tnel tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on ap-veth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 192.168.0.1 > 192.168.0.10: ICMP echo request, id 4873, seq 1, length 64 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff, ethertype ARP (0x0806), length 42: Request who-has 192.168.0.1 tell 192.168.0.3, length 28 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype ARP (0x0806), length 42: Reply 192.168.0.1 is-at 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, length 28 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 192.168.0.10 > 192.168.0.1: ICMP echo reply, id 4873, seq 1, length 64
確かに lo につけた IP アドレスへの ping が lo 以外のインターフェースでも受け取れることが分かりました。手動で設定した ARP テーブルのレコードは以下のコマンドで削除できます。
$ sudo ip netns exec client ip neigh del 192.168.0.10 dev client-veth0 $ sudo ip netns exec client ip neigh $
ロードバランサー(バーチャルサーバー)の設定
ここまで来ればあとは消化試合です。まずは lb に VIP を付与します。
$ sudo ip netns exec lb ip addr add 192.168.0.10 dev lb-veth0
$ sudo ip netns exec lb ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
15: lb-veth0@if14: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 2a:49:35:8b:02:70 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 192.168.0.2/24 scope global lb-veth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 192.168.0.10/32 scope global lb-veth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::8cd8:6dff:fe37:c463/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
$
Direct Routing の実装として Linux Virtual Server の IPVS を利用します。VIP の80番ポートを ap に転送することにしました。
$ sudo ip netns exec lb ipvsadm -A -t 192.168.0.10:80 $ sudo ip netns exec lb ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.0.10:80 -r 192.168.0.3 -g $
オプションの意味を以下に示します。
- -A … サービスを追加する
- -t … 追加するサービスとして TCP とバーチャルアドレスとポートを指定する
- -a … リアルサーバーを追加する
- -r … 追加するリアルサーバーのリアルアドレスを指定する
- -g … Direct Routing を使う(デフォルトなので省略可)
状態を確認すると以下のようになっています。
$ sudo ip netns exec lb ipvsadm -L IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096) Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags -> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn TCP 192.168.0.10:http wlc -> 192.168.0.3:http Route 1 0 0 $
動作確認
通信ができていることを確認するために ap で HTTP サーバーを立てます。
$ cat index.html Hello $ sudo ip netns exec ap python3 -m http.server 80 Serving HTTP on :: port 80 (http://[::]:80/) ...
client から VIP に curl を叩くと期待した結果が返ってきました。
$ sudo ip netns exec client curl -i 192.168.0.10 HTTP/1.0 200 OK Server: SimpleHTTP/0.6 Python/3.8.2 Date: Tue, 05 May 2020 12:59:47 GMT Content-type: text/html Content-Length: 6 Last-Modified: Tue, 05 May 2020 06:05:07 GMT Hello $
tcpdump で動きを確認しましょう。client では以下のようになりました。
$ sudo ip netns exec client tcpdump -tnel tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on client-veth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 2a:49:35:8b:02:70, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 74: 192.168.0.1.40464 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [S], seq 1358485123, win 64240, options [mss 1460,sackOK,TS val 3711481508 ecr 0,nop,wscale 7], length 0 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 74: 192.168.0.10.80 > 192.168.0.1.40464: Flags [S.], seq 2569087913, ack 1358485124, win 65160, options [mss 1460,sackOK,TS val 587559712 ecr 3711481508,nop,wscale 7], length 0 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 2a:49:35:8b:02:70, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40464 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [.], ack 1, win 502, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711481508 ecr 587559712], length 0 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 2a:49:35:8b:02:70, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 142: 192.168.0.1.40464 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [P.], seq 1:77, ack 1, win 502, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711481509 ecr 587559712], length 76: HTTP: GET / HTTP/1.1 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.10.80 > 192.168.0.1.40464: Flags [.], ack 77, win 509, options [nop,nop,TS val 587559713 ecr 3711481509], length 0 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 249: 192.168.0.10.80 > 192.168.0.1.40464: Flags [P.], seq 1:184, ack 77, win 509, options [nop,nop,TS val 587559713 ecr 3711481509], length 183: HTTP: HTTP/1.0 200 OK 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 2a:49:35:8b:02:70, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40464 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [.], ack 184, win 501, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711481509 ecr 587559713], length 0 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 72: 192.168.0.10.80 > 192.168.0.1.40464: Flags [P.], seq 184:190, ack 77, win 509, options [nop,nop,TS val 587559713 ecr 3711481509], length 6: HTTP 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 2a:49:35:8b:02:70, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40464 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [.], ack 190, win 501, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711481509 ecr 587559713], length 0 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.10.80 > 192.168.0.1.40464: Flags [F.], seq 190, ack 77, win 509, options [nop,nop,TS val 587559713 ecr 3711481509], length 0 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 2a:49:35:8b:02:70, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40464 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [F.], seq 77, ack 191, win 501, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711481510 ecr 587559713], length 0 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.10.80 > 192.168.0.1.40464: Flags [.], ack 78, win 509, options [nop,nop,TS val 587559714 ecr 3711481510], length 0 $
TCP の 3-way handshake の挙動は今回の主題ではないので無視してよいです。重要なのは client (7a:17:d9:30:82:46) → lb (2a:49:35:8b:02:70) への通信と ap (12:18:37:d7:29:5d) → client (7a:17:d9:30:82:46) への通信のみで構成されていて、client → ap や lb → client の通信が発生していないことです。
lb で確認すると以下のようになりました。
$ sudo ip netns exec lb tcpdump -tnel tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on lb-veth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 2a:49:35:8b:02:70, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 74: 192.168.0.1.40468 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [S], seq 2056074600, win 64240, options [mss 1460,sackOK,TS val 3711725842 ecr 0,nop,wscale 7], length 0 2a:49:35:8b:02:70 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 74: 192.168.0.1.40468 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [S], seq 2056074600, win 64240, options [mss 1460,sackOK,TS val 3711725842 ecr 0,nop,wscale 7], length 0 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 2a:49:35:8b:02:70, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40468 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [.], ack 2219513569, win 502, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711725842 ecr 587804046], length 0 2a:49:35:8b:02:70 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40468 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [.], ack 1, win 502, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711725842 ecr 587804046], length 0 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 2a:49:35:8b:02:70, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 142: 192.168.0.1.40468 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [P.], seq 0:76, ack 1, win 502, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711725842 ecr 587804046], length 76: HTTP: GET / HTTP/1.1 2a:49:35:8b:02:70 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 142: 192.168.0.1.40468 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [P.], seq 0:76, ack 1, win 502, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711725842 ecr 587804046], length 76: HTTP: GET / HTTP/1.1 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 2a:49:35:8b:02:70, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40468 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [.], ack 184, win 501, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711725843 ecr 587804047], length 0 2a:49:35:8b:02:70 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40468 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [.], ack 184, win 501, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711725843 ecr 587804047], length 0 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 2a:49:35:8b:02:70, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40468 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [.], ack 190, win 501, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711725844 ecr 587804048], length 0 2a:49:35:8b:02:70 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40468 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [.], ack 190, win 501, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711725844 ecr 587804048], length 0 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 2a:49:35:8b:02:70, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40468 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [F.], seq 76, ack 190, win 501, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711725844 ecr 587804048], length 0 2a:49:35:8b:02:70 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40468 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [F.], seq 76, ack 190, win 501, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711725844 ecr 587804048], length 0 7a:17:d9:30:82:46 > 2a:49:35:8b:02:70, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40468 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [.], ack 191, win 501, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711725845 ecr 587804049], length 0 2a:49:35:8b:02:70 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40468 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [.], ack 191, win 501, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711725845 ecr 587804049], length 0
lb では client (7a:17:d9:30:82:46) → lb (2a:49:35:8b:02:70) への通信を複製して lb (2a:49:35:8b:02:70) → ap (12:18:37:d7:29:5d) に流していることが分かります。
最後に ap での確認です。
$ sudo ip netns exec ap tcpdump -tnel tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on ap-veth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes 2a:49:35:8b:02:70 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 74: 192.168.0.1.40470 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [S], seq 2727864904, win 64240, options [mss 1460,sackOK,TS val 3711867194 ecr 0,nop,wscale 7], length 0 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 74: 192.168.0.10.80 > 192.168.0.1.40470: Flags [S.], seq 771200458, ack 2727864905, win 65160, options [mss 1460,sackOK,TS val 587945398 ecr 3711867194,nop,wscale 7], length 0 2a:49:35:8b:02:70 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40470 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [.], ack 1, win 502, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711867194 ecr 587945398], length 0 2a:49:35:8b:02:70 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 142: 192.168.0.1.40470 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [P.], seq 1:77, ack 1, win 502, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711867194 ecr 587945398], length 76: HTTP: GET / HTTP/1.1 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.10.80 > 192.168.0.1.40470: Flags [.], ack 77, win 509, options [nop,nop,TS val 587945398 ecr 3711867194], length 0 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 249: 192.168.0.10.80 > 192.168.0.1.40470: Flags [P.], seq 1:184, ack 77, win 509, options [nop,nop,TS val 587945398 ecr 3711867194], length 183: HTTP: HTTP/1.0 200 OK 2a:49:35:8b:02:70 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40470 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [.], ack 184, win 501, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711867194 ecr 587945398], length 0 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 72: 192.168.0.10.80 > 192.168.0.1.40470: Flags [P.], seq 184:190, ack 77, win 509, options [nop,nop,TS val 587945399 ecr 3711867194], length 6: HTTP 2a:49:35:8b:02:70 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40470 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [.], ack 190, win 501, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711867195 ecr 587945399], length 0 2a:49:35:8b:02:70 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40470 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [F.], seq 77, ack 190, win 501, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711867195 ecr 587945399], length 0 12:18:37:d7:29:5d > 7a:17:d9:30:82:46, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.10.80 > 192.168.0.1.40470: Flags [F.], seq 190, ack 78, win 509, options [nop,nop,TS val 587945400 ecr 3711867195], length 0 2a:49:35:8b:02:70 > 12:18:37:d7:29:5d, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 66: 192.168.0.1.40470 > 192.168.0.10.80: Flags [.], ack 191, win 501, options [nop,nop,TS val 3711867196 ecr 587945400], length 0
lb (2a:49:35:8b:02:70) → ap (12:18:37:d7:29:5d) という通信が来ていますが、戻りのパケットは ap (12:18:37:d7:29:5d) → client (7a:17:d9:30:82:46) と lb を経由せずに直接返していることが分かります。
まとめ
Network Namespace 上で Direct Routing 方式のロードバランサーを構築して tcpdump で動きを確認しました。
この記事では クリエイティブ・コモンズ 表示 4.0 国際 ライセンス のもとで SAKURA internet Inc. から提供されている さくらのアイコンセット を利用しています。
